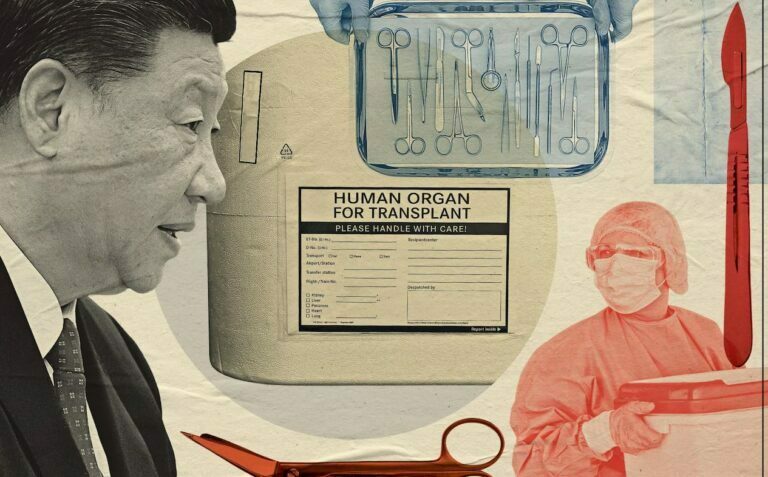
Uyghur Genocide: China faces Human Rights investigations over forced organ harvesting
By Ali Iqbal, Transplant Nephrologist, Assistant Professor of Medicine, McMaster University; and Aliya Khan, Clinical professor, Faculty of Health Sciences, McMaster University Organ transplantation is a life-saving therapy for millions of patients and one of the greatest successes of modern medicine. However, a limited supply of donor organs, paired with a massive demand for transplants,…